Not all heroes wear capes.
Some are just ordinary Americans who know a powerful secret about money.
And they use it to save their families thousands.
What's The Secret?










Some are just ordinary Americans who know a powerful secret about money.
And they use it to save their families thousands.
What's The Secret?
















* Publications in which GetSure has appeared in 2023.
The Problem
Dying Is Not Cheap...
... In total, American final expenses averaged $17,199 last year*
* "The Cost of Dying in 2023" Report
The Options
Buy Money Now...Or Later
If your family doesn't have $17,199 in savings, someone is going to have to buy money...
The Secret!
The Reality
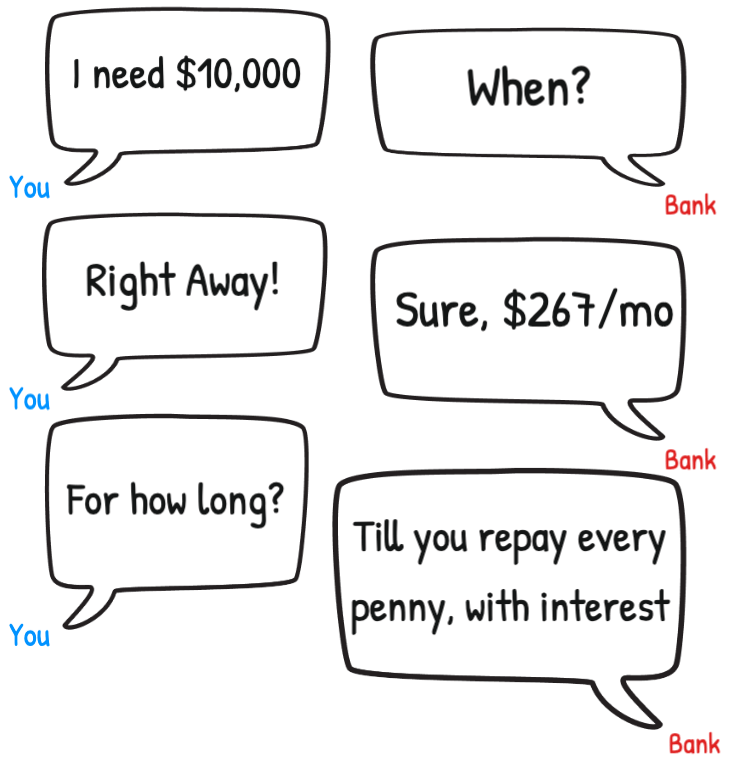
Note: It costs the average American $267/month over 60 months to repay $10,000 of credit card debt. That's $15,810.26 in total (source)
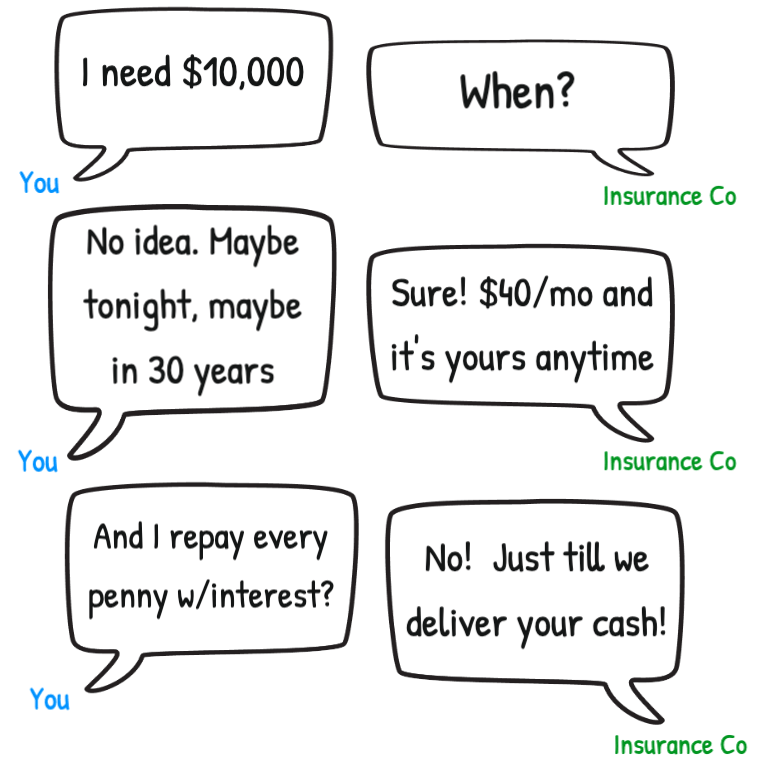
Note: Rate is for a 65-year-old woman. Total paid is calculated over her remaining life expectancy (of 19.7 years, according to the Social Security Administration) (source)
The math says insurance beats debt
any day of the week...
And is there a better or fairer
salesman than
math ?

Hello! We’re Martha and Rikin Shah, and we’re thrilled to welcome you to GetSure!
We’re a family business and independent life insurance agency licensed in all 50 states (plus D.C.).
We sell term and whole life insurance to Americans ages 0-90, and we’ve partnered with 19 insurance companies to do so.
Our motto internally is "do
small things with great love". If we have the opportunity to work with you, we hope you'll see that
before long.
Warm regards,
Rikin & Martha Shah
Co-Founders, GetSure
Choose kindness.
You never know what battles people may be fighting.